(Part I) Indian Physical Geography - The Northern Mountains (Himalayas) and The Northern plains |

|
|
Support us : https://www.instamojo.com/@exambin/
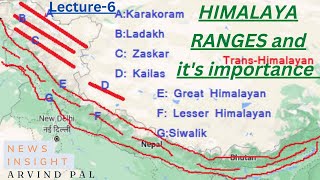
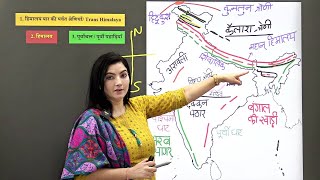
Download our app : http://examb.in/app Indian geography part 1 Indian Physical Geography – The Northern Mountains (Himalayas) India can be divided into 6 major physical divisions The Northern Mountains ( himalayan geography ) The North Indian Plain ( northern plains of india ) The Peninsular Plateau Great Indian Desert The coastal Regions Islands The session on indian geography lecture for ias in english will be useful for indian physical geography upsc questions and indian physical geography ssc questions. ________________________________________ The Himalayan Mountains form the northern mountain region of India. They are the highest mountain ranges in the world. These mountain ranges start from Pamir Knot in the west and extend up to Purvanchal in the east. Himalayas are the Youngest & Loftiest mountain range of the world Formed by Tectonic Forces and it ranges upto 2400 Km in Length Are of varying width → from 400 Km in Kashmir to 160 Km Arunachal Pradesh Altitudinal variations are greater in the eastern part than in the western part Prominent Features → Highest peaks, Deep valleys & Gorges, Glaciers etc. Indian physical features are discussed in brief in the session. The Himalayan Mountains can be further divided into 4 major ranges - Trans Himalayas Immediate to the north of the Great Himalayan Range Most of the part of this Himalayan range lies in the Tibet and hence also called Tibetan Himalaya Ranges → Zaskar, K2 (Godwin Austin), Ladakh, Kailash and Karakoram Range Greater Himalaya (Inner Himalaya) Always covered with snow → Known as Himadri Average height → 6000 mts Most continuous range Core composed of granite Ranges → Mt. Everest, Kanchenjunga Forests type → Needle leaved coniferous Middle Himalaya Average height → 3500 – 4500 mts Most of the valleys & hill stations are located in this range e.g. Kashmir, Kathmandu , Nainital Ranges → Pir Panjal, Dhaula Dhar, Mahabharat ________________________________________ Eastern hills / Purvanchal Brahmaputra marks the eastern border of the Himalayas. Beyond the Dihang gorge, the Himalayas bend sharply towards south and form the Eastern hills or Purvanchal which run through the NE India & are mostly composed of sandstones These hills comprises of Mishmi hills, Patkai Hills, Naga Hills, Manipuri Hills and Mizo Hills Classification of Himalayas on the basis of Geographic Location Punjab Himalayas / Kashmir Himalaya / Himachal Himalaya → Between the Indus and Sutlej Kumaon Himalayas → Between Sutlej and Kali rivers Nepal Himalayas → Between Kali and Tista rivers Assam Himalayas → Between Tista and Dihang rivers ________________________________________ Significance of Himalayas for India Strategic significance Acts as a natural frontier of India with other countries (China, Pakistan, Afghanistan) Climatic significance Prevent further northward movement of summer monsoon and also prevent cold northern winds from Siberia to enter into India Indian Physical Geography – The Northern Indian Plains The North Indian Plain Formed by depositional work of Rivers viz. Indus, Ganga & Brahamputra 2400 km long & varying in width from 240 to approx. 320 km Divided into three sections, viz. the Punjab Plain (Indus), the Ganga Plain and the Brahmaputra Plain Punjab Plains Formed by the Indus and its tributaries with major portion of this plains in Pakistan ________________________________________ Northern plains subdivisions Bhabhar Lies along foothills of Shiwaliks, From Indus to Tista Laid down by streams coming from hills Comprises of pebble studded rocks (Highly porous bed plain) Due to high porosity, streams disappears here Tarai Lies south of Bhabhar & runs parallel to it Marked by re-emergence of underground streams of Bhabhar belt Highly alluvial & agricultural land Has a high water table due to groundwater percolating down from the adjacent zone Khadar Flood plains with newer alluvium deposited by flood almost every year Soil of this region is locally known as kankar viz. calcareous concretions With this we have come to the end of the session on indian geography lecture in english. We have seen the two important divisions of Indian Physical Geography. We will be seeing the rest of the divisions in our next video by next week. Thank you for watching till the end. Subscribe to our channel and click on the bell icon to get regular updates. |

Indian Geography-Mountains in India (भारत के पर्वत)/SSC/Railway/Delhi Police/ GK GS Live by Aman Sir

















![L3: Northern Mountain | Physiographic Division Indian Geography [Crack UPSC CSE 2020] Praveen Singh](https://ytimg.googleusercontent.com/vi/LiqfKp8w76M/mqdefault.jpg)








