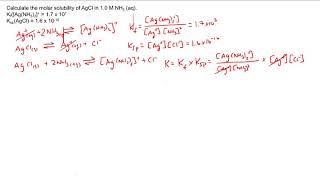Complex Ion Formation | MCAT Organic Chemistry Prep |

|
|
Need help preparing for the General Chemistry section of the MCAT? MedSchoolCoach expert, Ken Tao, will teach everything you need to know about the complex ion formation of solutions. Watch this video to get all the MCAT study tips you need to do well on this section of the exam!
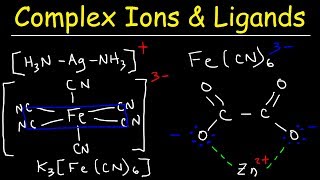
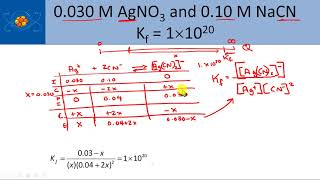
You’re already familiar with simple ion pairs, for instance, the interaction of sodium cation and chloride anion to form table salt. Additionally, more nuanced ions known as complex ions can also be formed. In contrast to simpler ions, these ions are notable for the presence of multiple ligands and covalent bonds. They have a key function that we should note – they can drastically increase the solubility of a compound in solution. Formation of a Complex Ion Complex ions are formed through the donation of an electron pair by a Lewis base to a Lewis acid. Typically, the Lewis acid is a metal cation and the Lewis base is a ligand. Next, there is a reaction describing the formation of a complex ion. The equilibrium constant for the reaction is what we call the formation constant (Kf). Determining the expression for Kf is identical to determining the expression for any other reaction (products/reactants). In the multi-step reaction during which a complex ion is formed, each step has its own equilibrium constant. The formation constant of the reaction is equal to the product of the equilibrium constants of each step. The case of a complex ion being formed from copper and ammonia is shown below. Utility of a Complex Ion The reason why complex ions are important is because they can drastically increase the solubility of a compound by removing a common ion. Let's take a look at an example: in a solution containing Cu(OH2), how will the addition of ammonia affect the dissolution of Cu(OH2)? The relevant equilibriums are shown below. First we note that the Ksp for copper hydroxide is very small. This is common in this sort of problem, where the Ksp of the non-complex ion equilibrium is relatively small. Therefore, most of the copper is initially in the form of the precipitate, copper hydroxide. On the other hand, Kf is often very large, as it is in this case. Since this is very favorable, adding ammonia to solution will cause a large amount of ammonia-copper complex to form, pulling lots of copper ions away from the solution. Applying Le Chatelier's principle, a decrease in the concentration of copper cation will drastically stimulate the dissolution of copper hydroxide. This demonstrates the essence of complex ion formation: complex ion formation will use up many of the ions in solution (in this case, copper), forcing other ion pairs in solution to dissolve to a much greater extent. MEDSCHOOLCOACH To watch more MCAT video tutorials like this and have access to study scheduling, progress tracking, flashcard and question bank, download MCAT Prep by MedSchoolCoach IOS Link: https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=com.htd.medschoolcoach&hl=en_US Apple Link: https://apps.apple.com/us/app/mcat-prep-by-medschoolcoach/id1503000883 #medschoolcoach #MCATprep #MCATstudytools |