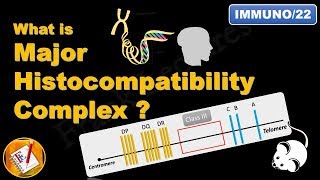
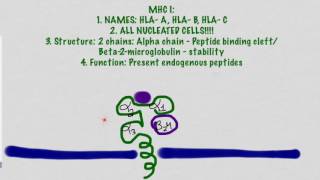
Introduction to Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC) | MHC Class-1, 2, 3 | Basic Science Series |

|
|
0:00 Introduction
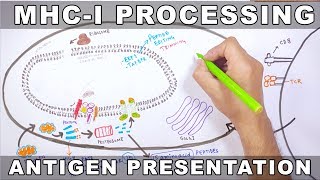
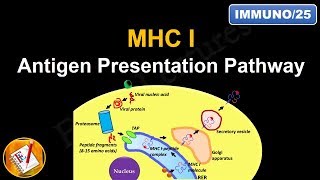
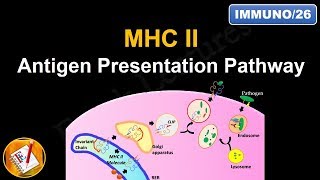
0:22 Importance 0:43 Classification 1:04 Role 1:22 Other Name 1:29 Determination 1:47 Main function 1:57 Interaction 2:07 Epitope 2:26 Sub-Groups 2:35 MHC Class 1 2:50 MHC Class 2 3:07 MHC Class 3 3:32 Conclusion 3:53 Coming soon SEO Keywords: MHC class 1, MHC Class 2, MHC Class 3, MHC Class 1 and 2 difference, MHC Class 1 Structure, MHC Class 1 and 2 Structure, MHC class 2 structure, MHC function, MHC Class 1 function, MHC Class 2 function, Major Histocompatibility Complex ppt, Major Histocompatibility Complex notes, Major Histocompatibility Complex notes pdf, Major Histocompatibility Complex is quizlet, Major Histocompatibility Complex function, Major Histocompatibility Complex definition, Major Histocompatibility Complex (mhc), MHC class 1 proteins, MHC class II proteins, MHC 1 and 2 structure, MHC 1 and 2 structure and function, MHC 1 and 2 function, MHC 1 and 2 antigen processing pathway, MHC 1 and 2 immunology. Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC) introduction | MHC Class-1, 2, 3 | | Basic Science Series In this presentation, we will focus on the structure and function of major histocompatibility complex class-1 molecules in detail. We will also know about the interaction with CD 8 co-receptor and the function of various domains of MHC class-1 molecule. So please watch the full presentation to understand the structure and functions of the MHC class-1 molecule. Definition: The Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC), also known as the Human Leukocyte Antigen (HLA) system in humans, is a group of genes that encode cell surface proteins responsible for presenting antigens to the immune system. Genetic locus: The MHC is located on chromosome 6 in humans and is highly polymorphic, meaning it exhibits extensive genetic variation between individuals. Types of MHC molecules: There are two main classes of MHC molecules: MHC class I and MHC class II. MHC class I molecules: MHC class I molecules are expressed on the surface of almost all nucleated cells in the body. They present antigens derived from intracellular pathogens, such as viruses and some bacteria, to cytotoxic T cells (CD8+ T cells). MHC class II molecules: MHC class II molecules are primarily expressed on the surface of antigen-presenting cells (APCs) such as macrophages, dendritic cells, and B cells. They present antigens derived from extracellular pathogens to helper T cells (CD4+ T cells). Antigen presentation: MHC molecules bind to antigens, which are fragments of proteins from pathogens, and display them on the cell surface. This process is known as antigen presentation. Recognition by T cells: T cells have receptors called T cell receptors (TCRs) that can recognize specific antigens displayed by MHC molecules. CD8+ T cells recognize antigen-MHC class I complexes, while CD4+ T cells recognize antigen-MHC class II complexes. Role in immune response: MHC molecules play a crucial role in the adaptive immune response by allowing T cells to recognize and respond to foreign antigens. They are essential for the activation and coordination of immune cells during infection or other immune challenges. MHC polymorphism: The MHC genes are highly polymorphic, meaning there are many different versions or alleles of these genes within a population. This polymorphism allows for a wide range of antigen presentation and enhances the immune system's ability to recognize a diverse array of pathogens. Transplantation compatibility: MHC compatibility is a critical factor in organ and tissue transplantation. The recipient's immune system must be compatible with the MHC molecules of the donor to avoid rejection of the transplanted tissue. Support my work at https://www.patreon.com/user?u=37177596 Twitter: https://twitter.com/DrKumarLokender Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/lokenderkumar.sharma Linkedin: https://www.linkedin.com/in/dr-lokender-kumar-58525945/ Disclaimer: The information provided is for educational purposes only. The content of this channel should not be considered as medical advice of any kind. Please consult your doctor for medical help. Use this information at your own risk. We hold no responsibility for any issue, concerns, or damage arising from the content of the video. Under no circumstances Basic Science Series English be responsible or liable in any way for any content, including but not limited to, any errors or omissions in the content, any loss, any damage of any kind incurred as a result of any content communicated in this video, whether by Basic Science Series English or a third party. In no event shall Basic Science Series English be liable for any special indirect or consequential damages of any damages whatsoever resulting from the content of our channel. |